Charles R. Goulding and Preeti Sulibhavi examine the progress of Fabric8Labs and its ECAM technology.
Scaling electrochemical additive manufacturing technology is no easy task. But Fabric8Labs, Inc is doing just that and, at a time, when start-ups are having difficulty raising capital. In fact, Fabric8Labs just closed a US$50M Series B investment round led by New Enterprise Associates (NEA). NEA is a global venture capital firm focused on helping entrepreneurs build transformational businesses across multiple verticals. Since the firm’s founding, there has been nearly US$24B in cumulative committed capital and more than 270 portfolio company IPOs.
Fabric8Labs has garnered much attention and has received funding from some big-name sources such as Mark Cuban and Intel. The February 8th, 2023, Wall Street Journal described the fact that 2022 was a record year for 3D printing venture capital funding and Fabric8Labs continues the trend in January 2023.
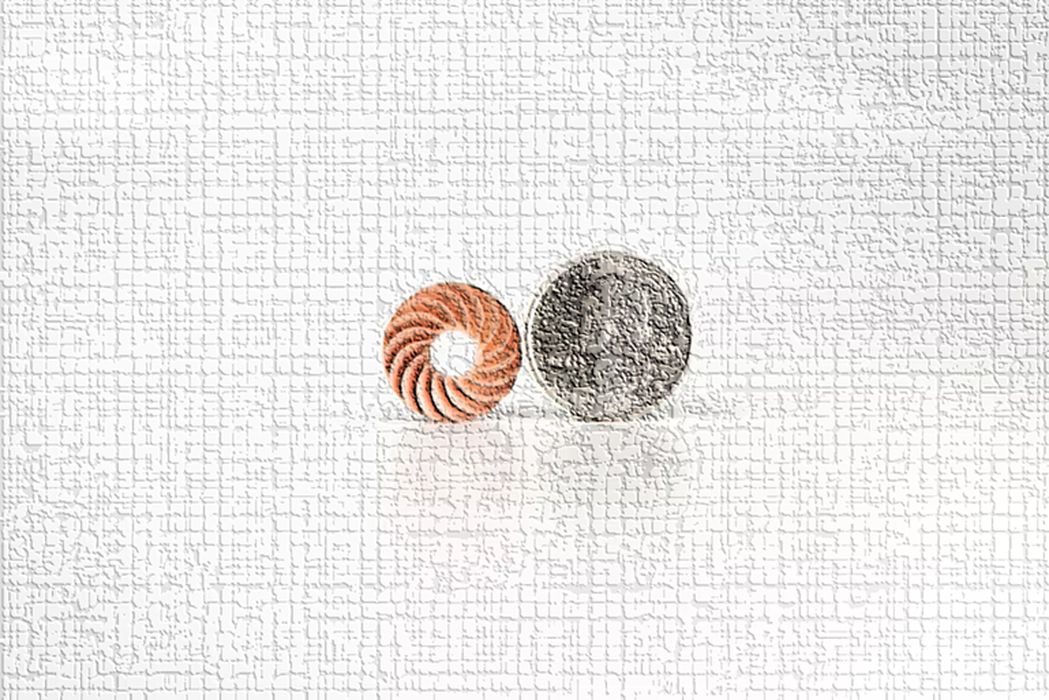
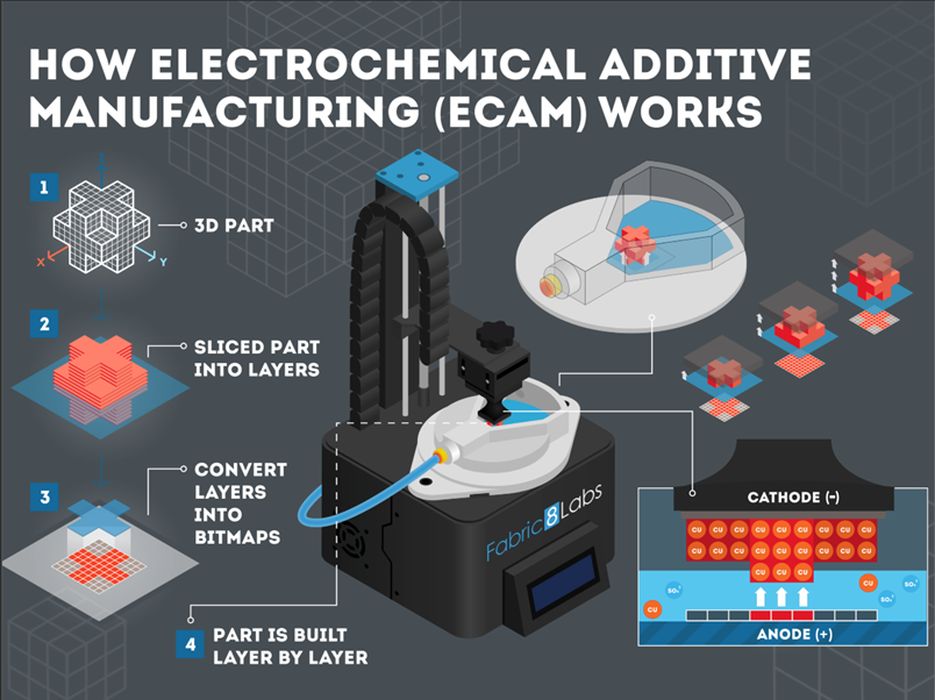
The company is primarily involved in metal 3D printing, without using powders. Fabric8Labs’ proprietary Electrochemical Additive Manufacturing technology enables the company to economically 3D print highly complex components for its top target markets that include semiconductor heat sinks and radio frequency antenna parts.
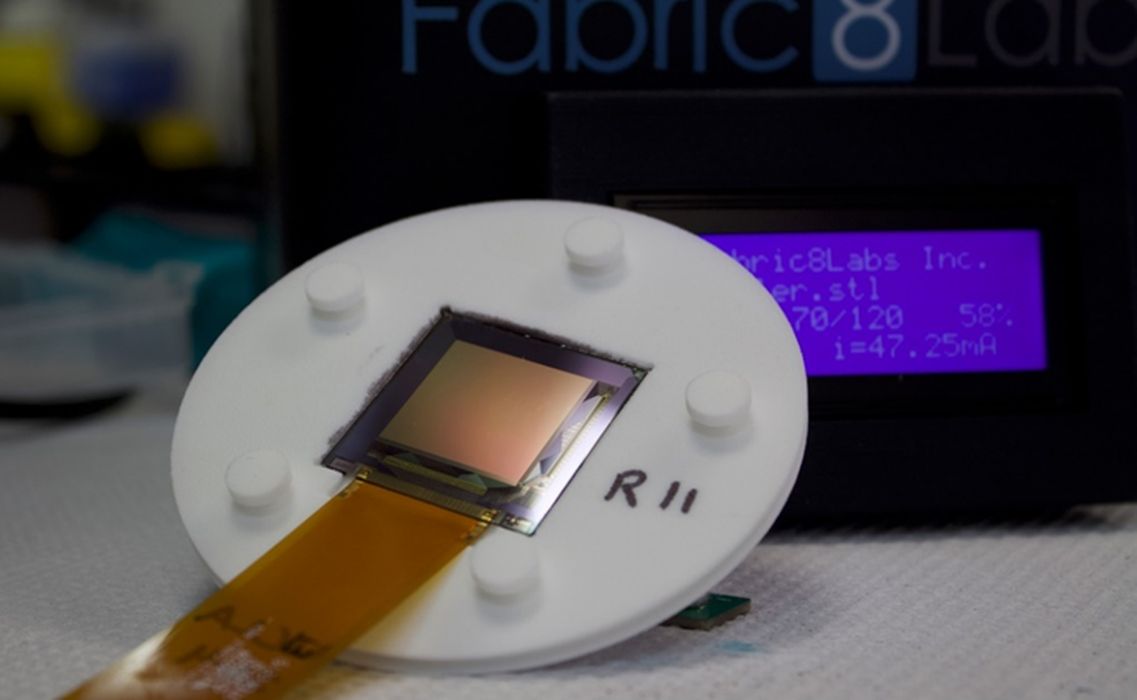
Fabric8 uses a unique process to develop parts and a control system that is less expensive than metal printing technologies and infinitely recyclable. It’s high-speed, faster than regular lasers and versatile to print many different types of materials because it uses no heat.
Their proprietary technology involves electrochemical deposition, eliminating the need for expensive metal powders, vacuum chambers, and lasers. Parts produced using ECAM are built at the atomic level leading to higher resolution features, 99.9%+ part densities, and mirror-like surface finishes.
This process is referred to as Electrochemical Additive Manufacturing or ECAM. Fabric8Labs has the financial backing of SE Ventures, TDK Ventures, and Lam Capital as well, all of whom are excited about the ECAM’s end applications for high-performance computing, data centers, electric vehicles, wearables, RF communications and a wide range of consumer electronics products.
The Research & Development Tax Credit
The now permanent Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit is available for companies developing new or improved products, processes and/or software.
3D printing can help boost a company’s R&D Tax Credits. Wages for technical employees creating, testing and revising 3D printed prototypes can be included as a percentage of eligible time spent for the R&D Tax Credit. Similarly, when used as a method of improving a process, time spent integrating 3D printing hardware and software counts as an eligible activity. Lastly, when used for modeling and preproduction, the costs of filaments consumed during the development process may also be recovered.
Whether it is used for creating and testing prototypes or for final production, 3D printing is a great indicator that R&D Credit eligible activities are taking place. Companies implementing this technology at any point should consider taking advantage of R&D Tax Credits.
Conclusion
We are just as excited as these big-name investors to see Fabric8Labs succeed. It would be a big deal for the advancement of 3D printing as well as for the wide array of industries that Fabric8Labs’ products impact.
