![[Source: Jabil ]](https://fabbaloo.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Robots-Image3_img_5eb0a0518cb4c.png)
Charles Goulding and Ian Brown of R&D Tax Savers discuss 3D printing in the robotics industry.
The December 1st, 2nd issue of the Wall Street Journal contained a thought provoking article entitled “Why Aren’t There More U.S. Robots?”
The accompanying table to the article (see below) demonstrates that the U.S. is far behind in the global robot adoption rate.
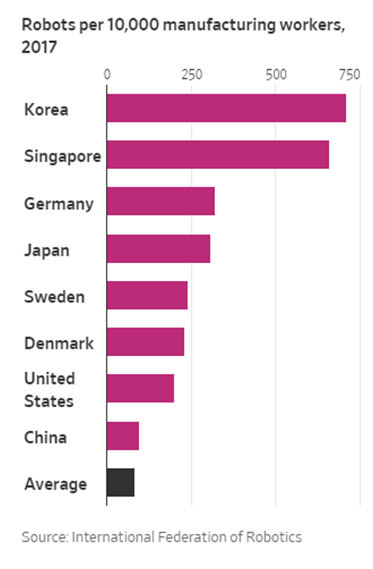
Although the U.S. leads in 3D printing, it severely lags in the adoption of robot automation technology. Richard D’Aveni, the Dartmouth professor, in his new book entitled The Pan Industrial Revolution believes that prospectively the world will evolve into a pan industrial digital economy with huge enterprises that integrate 3D printing, robots and machine tools.
This future prediction is most certainly dependent on large increases in U.S. robot installations, as an integrated pan industrial system is only as effective as its weakest link. Our firm analyzes robot projects in 4 major categories as presented in our Robot Quartet article series.
As the 3D printing industry evolves from lower-volume design applications to large production volumes, closing the robot gap becomes ever more critical. High-volume 3D production requires robots to handle component manufacturing and installation, as well as for picking and packing.
R&D tax incentives can be used to support both robot and 3D printer product improvements and process integration necessary for the transcendence of the new Pan Industrial economy. Prime examples of robot 3D printer integration at the smaller company level and the larger company level are Voodoo Manufacturing and Jabil.
The Research & Development Tax Credit
Enacted in 1981, the now permanent Federal Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit allows a credit that typically ranges from 4%-7% of eligible spending for new and improved products and processes. Qualified research must meet the following four criteria:
-
New or improved products, processes, or software
-
Technological in nature
-
Elimination of uncertainty
-
Process of experimentation
Eligible costs include employee wages, cost of supplies consumed in the R&D process, cost of pre-production testing, US contract research expenses, and certain costs associated with developing a patent.
Voodoo Manufacturing
![[Source: CNBC ]](https://fabbaloo.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Robots-Image2_img_5eb0a0526071d.png)
Founded in 2015, Voodoo Manufacturing is a leading additive manufacturing company based in Brooklyn, New York. The company is comprised of industry and technology experts who are dedicated to allowing businesses of all sizes to produce products inexpensively and in the USA. The company currently has over 200 printers working around the clock to achieve this goal.
At the beginning of their operations, Voodoo Manufacturing was the victim of their own success. In order for the team to keep up with their rapid growth, they needed to automate the loading and unloading operations to be able to handle the massive volumes and orders. In 2017, Voodoo Manufacturing announced that they planned to integrate robots into their 3D printing factory floor. Voodoo purchased and integrated robots and other robot components from Universal Robots, a leading manufacturer of collaborative robots. Voodoo Manufacturing has implemented the UR10 from Universal Robots on their manufacturing floor. These robots can take a plate out of the printer, put a new one in and restart the printer to begin the next job. These robots can work continuously with very minimal need for human intervention and supervision. Upon integration of the robots, the team was able to triple their production and cut startup costs by 90 percent.
Jabil Inc.
Jabil Inc. is a leading global manufacturing services company. The company creates solutions for their clients’ manufacturing in a multitude of industries, including automotive, healthcare/pharmaceutical/medical devices, defense/aerospace, transportation, and smarthome to name a few. Since 2014, the company has been incorporating robotic and 3D printing capabilities into their client solutions.
Jabil recognizes the importance of offering new technology and solutions to their customers, including additive manufacturing, robotics and fully autonomous systems. Manufacturers who have partnered with Jabil have experienced significant improvements in their efficiency and operations. Full integration of robotics and autonomous systems includes a package that allows warehouses and factories to inspect their systems in real time, implement “smart sensors” which provide feedback and insight for preventive maintenance, and aggregation of IoT. For more information on Jabil and their 3D printing activities, read our other Fabbaloo article titled “Jabil: A Leader in 3D Printing And A Pioneer Of Industry 4.0”
Conclusion:
Although the United States currently lags behind the rest of the world in terms of robot installation, companies can utilize the R&D Tax Credit to reduce the costs of implementation and integration of these robots into operations.










A manufacturing-as-a-service company has developed a way to 3D print continuous carbon fiber in a production setting.